Maybe having a mortgage is going out of fashion now that the affluent have taken over real estate? Or do we just need to Get Good Help with filing taxes? (30%-40% of Americans prepare their own taxes)
The mortgage-interest deduction, a beloved tax break bound tightly to the American dream of homeownership, once seemed politically invincible. Then it nearly vanished in middle-class neighborhoods across the country, and it appears that hardly anyone noticed.
In places like Plainfield, a southwestern outpost in the area known locally as Chicagoland, the housing market is humming. The people selling and buying homes do not seem to care much that President Trump’s signature tax overhaul effectively, although indirectly, vaporized a longtime source of government support for homeowners and housing prices.
The 2017 law nearly doubled the standard deduction — to $24,000 for a couple filing jointly — on federal income taxes, giving millions of households an incentive to stop claiming itemized deductions.
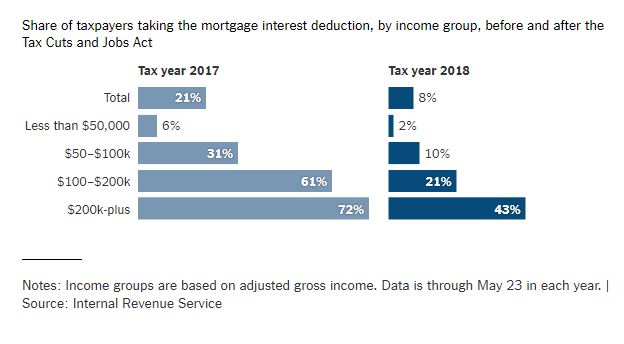
As a result, far fewer families — and, in particular, far fewer middle-class families — are claiming the itemized deduction for mortgage interest. In 2018, about one in five taxpayers claimed the deduction, Internal Revenue Service statistics show. This year, that number fell to less than one in 10. For families earning less than $100,000, the decline was even more stark.
The benefit, as it remains, is largely for high earners, and more limited than it once was: The 2017 law capped the maximum value of new mortgage debt eligible for the deduction at $750,000, down from $1 million. There has been no audible public outcry, prompting some people in Washington to propose scrapping the tax break entirely.
For decades, the mortgage-interest deduction has been alternately hailed as a linchpin of support for homeownership (by the real estate industry) and reviled as a symbol of tax policy gone awry (by economists). What pretty much everyone agreed on, though, was that it was politically untouchable.
Nearly 30 million tax filers wrote off a collective $273 billion in mortgage interest in 2018. Repealing the deduction, the conventional wisdom presumed, would effectively mean raising taxes on millions of middle-class families spread across every congressional district. And if anyone were tempted to try, an army of real estate brokers, home builders and developers — and their lobbyists — were ready to rush to the deduction’s defense.
Now, critics of the deduction feel emboldened.
“The rejoinder was always, ‘Oh, but you’d never be able to get rid of the mortgage-interest deduction,’ but I certainly wouldn’t say never now,” said William G. Gale, an economist at the Brookings Institution and a former adviser to President George H.W. Bush. “It used to be that this was a middle-class birthright or something like that, but it’s kind of hard to argue that when only 8 percent of households are taking the deduction.”
Link to Full NYT Article



The evil is that interest expense continues to be business deductible that is now almost gone for mere people. The Tax Reform Act of 1986 started it and the HMID is the last [battered] bastion remaining.
I predicted before the Great Recession that we were headed here and that the reason the very rich didn’t care was because they’d just start renting their domiciles from an LLC whose sole asset was a mansion. [Or a mansion and vacation home and pied-à-terre in NYC and…].
I suspect that most of the 21% still taking HMID are single, so have a $12k std deduction.
It is difficult to get over $24k for a couple with the SALT $10k limit.
So only the very rich, and singletons, are still using HMID.
The owner-occupiers with mortgages between $700,000 and $1,000,000 are paying at least $24,000 per year in mortgage interest. Why wouldn’t them itemize to take the full deduction?
Either there is some ignorance among those folks about their tax preparation, or there are substantially fewer of them now?
The $750,000 cap applies only to those who got their mortgage since 1/1/2018.